[UI/UX] SDLC Model - Deep Dive Into the Agile Model
Software Development Life Cycle, SDLC, Agile, Sprint, Interaction Design, UI, UX
Introduction
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a framework that helps companies fine-tune their product and develop a product that meets user requirements. Companies can make decisions on how they want to design their product, how they will maintain and how the end-users will interact with the product. The major goal is to enhance the user experience.
SDLC has four(4) common activities, and these are also called the four(4) common activities of an interaction design.
Discovering Requirements
Focus on discovering new ideas/solutions and users' needs.
Define what will be developed.
Understand the background information, needs and interaction goals.
Purpose
Understand the targeted users.
Identification of design errors.
Create an interactive product that can support the object.
Designing Alternatives
Design a series of user experience flows and layouts based on the requirements
Purpose
Generate better alternatives.
Providing ideas that can satisfy user requirements.
Can be used for getting feedback.
Better explanation of design concepts.
Prototyping
Creating a prototype of a product that users can actually interact with.
Purpose
- Enables users interactivity, evaluation of the product, problem identification and actual UX with the product.
Evaluating
Gathering feedback/reviews of a product design.
Purpose
Determines the usability and acceptability of the product.
Design measured in terms of a variety of usability and user experience criteria.
General SDLC:
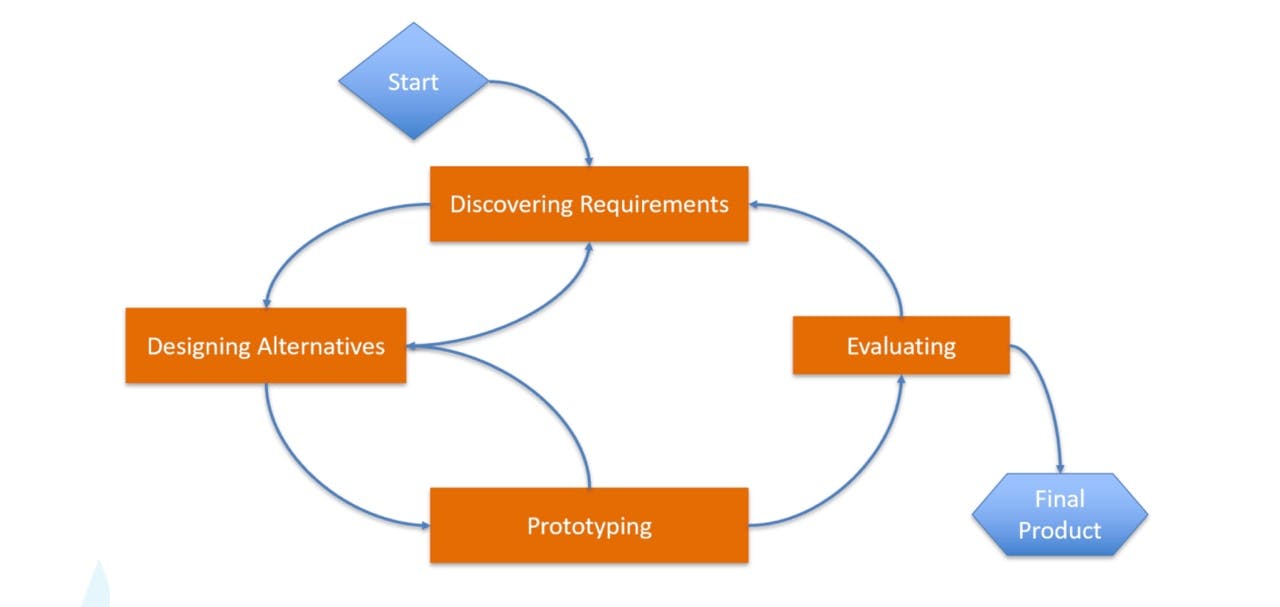
Most SDLC models have this kind of structure, it usually starts with identifying requirements -> designing the product -> prototyping (getting feedback) -> Evaluating. Some of the stages are iterative to ensure a successful product.
Now you have an idea of what the SDLC looks like and what stages it has, let's have a look at this photo:
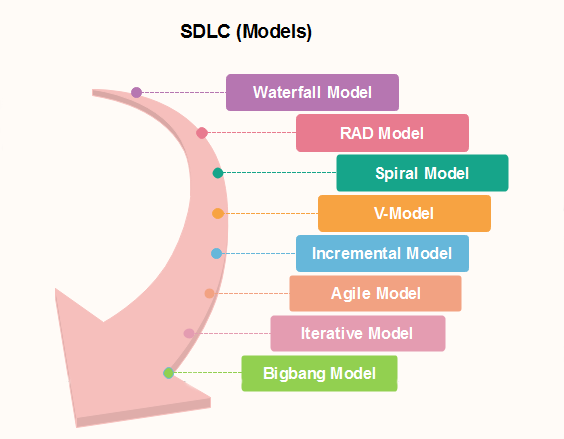
There are many SDLC models. I will briefly explain some of them. The main focus of this article is the agile model.
Waterfall Model: The traditional and old SDLC model.
Spiral Model: Risk-driven model, meaning that the focus is on managing risk through multiple iterations of the software development.
V-model: Variation of the waterfall model. Emphasizes product quality and testing.
Incremental Model: Requirements are divided into multiple standalone modules of the software development cycle.
Agile Model: Allows a company to adapt quickly to change requests.
Agile Model
The goal of an agile lifecycle model is to meet users’ requirements in a way that is quick and efficient. The Agile model is suitable for short-term projects. So, it has the benefit that the developer team does not waste time like a year to develop a product that will eventually fail in the market. Some other life cycle model is for long-term project and requires at least a year.
The principle of an agile model is that it investigates and communicates with users to identify the user requirements rather than fully relying on the team members and employees. Therefore, it follows a user-centered approach where users are involved throughout the entire development process. This can eventually lead to a product that satisfies users.
As the main aim of the agile model is to meet user requirements and develop a successful product in a short period of time, "agility" is required. Agility is achieved by fitting the process to the project and removing activities that may not be essential for a specific project. Also, anything that leads to a waste of time is avoided.
Advantages
Customer satisfaction through rapid, continuous delivery of useful products is possible.
People and user interactions are the focus rather than processes and tools.
- Customers, developers and testers constantly interact with each other.
There is a regular adaptation to changing circumstances.
Even if late changes come up, requirements are welcomed during the processing.
Stages
Agile Model:
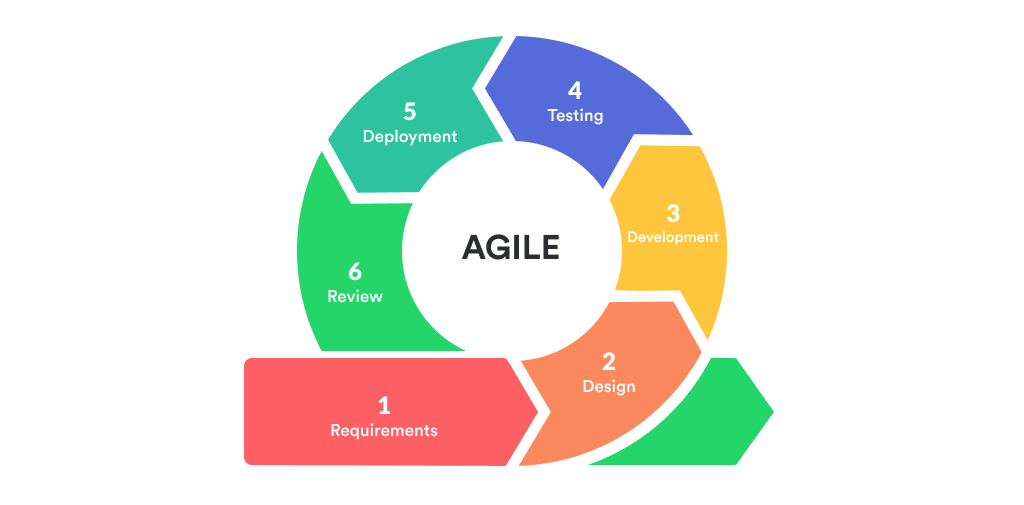
There are six(6) phases in the agile model. These six(6) phases can be revised several times through iterative processes. So, the one circle is the first iteration, and there can be more iterations if needed.
Requirements
Involves brainstorming to determine the user's requirements.
Identifies who are the users, how users will use the product as well as the cost and time required for the completion of the product development.
Identifying targeted ensures that our solutions are catered to the needs of the specific targeted users.
Design
Involves developing multiple alternatives based on the user's expectations and selecting the best design.
It is a stage where the problems with the current UX are evaluated to design a product that solves the current problems.
In this stage, conceptual models can be created to choose among alternatives.
Development
Involves prototyping, a process that turns the conceptual model into an actual and functional object that users can actually interact with.
The developer team can identify how users interact with the product and gather feedback from the users.
Testing
Requires the team to conduct several tests to ensure the quality, functionality and reliability of the product (i.e. developer-side testing).
A process where the product goes through quality assurance checks before the product is released.
Deployment
A phase where the product is launched and made available to end users.
Allows users to start testing the device.
Feedback is gathered, which allows the developer team to identify current problems and solve the issue.
Review
After releasing the product, the team can work together to go through the feedback and come up with new ideas based on the gathered feedback.
This stage is important as it ensures the success of the solution.
If a bug occurs, the team must consider an update for the device.